Home » Our Services » Tonsils/Adenoids
Tonsils/Adenoids
Tonsils
The palatine tonsils are located on each side of the throat, at the back of the tongue. They are similar to lymph nodes and serve as part of the immune system. Because of their function, tonsils often become inflamed or infected. Some tonsils create small crypts which are similar to pores and can produce tonsil stones which are small white, often foul smelling/tasting, stones. It is uncommon but the tonsils can develop cancers. Large tonsils can also cause snoring or sleep apnea. This is more common in children but can also occur in adults. If the tonsils create problems then they may need to be removed surgically. If tonsils are removed completely, they should not grow back.
Adenoids
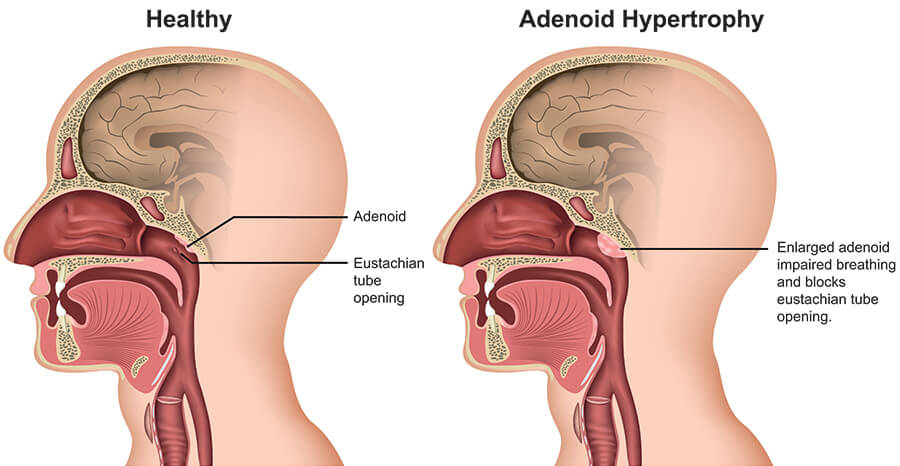
The adenoids are like tonsils but in the back of the nose. They also can get inflamed or infected and can grow to the point they block the back of the nose. By blocking the back of the nose, enlarged adenoids can make breathing through the nose difficult or can make the nose runny. They can also block the opening of the eustachian tube which connects the middle ear to the back of the nose. This can increase the risk of ear infections, ear popping or ear pressure. It is uncommon but the adenoids can also develop cancers. If adenoids are enlarged and causing problems then they may need to be surgically removed.
Tonsil/Adenoid Surgery
The tonsils and adenoids can be removed surgically through the mouth or sometimes the nose. Most patients who have their tonsils or adenoids removed can go home the same day. If a patient has certain risk factors then they may need to stay overnight in the hospital. The surgery usually takes about 30-45 minutes. Patients usually recover from surgery in about 2 weeks. After surgery patients will need to be on a soft food diet, meaning nothing that is hard, fried or crunchy to prevent scratching of the throat. The main risk of the surgery is bleeding afterwards. This risk is about 1-3%. A small amount of blood in the saliva is normal but if a patient has major bleeding they should be seen immediately. Most patients have a sore throat after surgery which can last about 2 weeks and is often treated with multiple types of pain medication. Once healing is complete, snoring and breathing should be improved and the patient should have less frequent and less severe throat infections.
If you believe your tonsils or adenoids are problematic, call to schedule a consultation today!